How A Photo voltaic system work
Simply put, PV systems are like any other electrical power generating systems, just the equipment used is different than that used for conventional electro mechanical generating systems. However, the principles of operation and interfacing with other electrical systems remain the same, and are guided by a well-established body of electrical codes and standards.
Although a PV array produces power when exposed to sunlight, a number of other components are required to properly conduct, control, convert, distribute, and store the energy produced by the array.
Depending on the functional and operational requirements of the system, the specific components required may include major components such as a DC-AC power inverter, battery bank, system and battery controller, auxiliary energy sources and sometimes the specified electrical load (appliances). In addition, an assortment of balance of system (BOS) hardware, including wiring, overcurrent, surge protection and disconnect devices, and other power processing equipment. Figure 3 show a basic diagram of a photovoltaic system and the relationship of individual components.
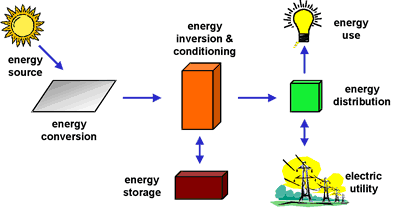
Figure 1. Major photovoltaic system components.
Why Are Batteries Used in Some PV Systems?
Batteries are often used in PV systems for the purpose of storing energy produced by the PV array during the day, and to supply it to electrical loads as needed (during the night and periods of cloudy weather). Other reasons batteries are used in PV systems are to operate the PV array near its maximum power point, to power electrical loads at stable voltages, and to supply surge currents to electrical loads and inverters. In most cases, a battery charge controller is used in these systems to protect the battery from overcharge and overdischarge.
Photovoltaics –
Photovoltaics (PV) is the field of technology and research related to the application of solar cells for energy by converting sunlight directly into electricity Due to the growing demand for clean sources of energy, the manufacture of solar cells and photovoltai array has expanded dramatically in recent years
Photovoltaic production has been doubling every two years, increasing by an average of 48 percent each year since 2002, making it the world’s fastest-growing energy technology. At the end of 2007, according to preliminary data, cumulative global production was 12,400 megawatts. Roughly 90% of this generating capacity consists of grid-tied electrical systems. Such installations may be ground-mounted (and sometimes integrated with farming and grazing) or built into the roof or walls of a building, known as Building Integrated Photovoltaic or BIPV for short.[
Net metering and financial incentives, such as preferential feed-in tariffs for solar-generated electricity, have supported solar PV installations in many countries including India , Australia, Germany, Israel,[ Japan, and the United States.
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js"></script>
<ins class="adsbygoogle"
style="display:block"
data-ad-format="fluid"
data-ad-layout-key="-63+c9+5c+c-65"
data-ad-client="ca-pub-8400181284928030"
data-ad-slot="4663670489"></ins>
<script>
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
</script>
