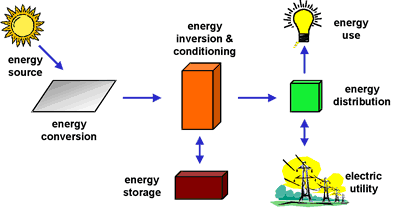
The sun produces an unbelievable amount of energy that reaches the earth. The amount of energy that is absorbed by the earth in one hour is more energy than mankind uses in one year. The total amount of solar energy reaching the earth in one year is huge – twice as much energy as ever existed from all sources of coal, oil, natural gas, and uranium combined. The sun strikes the surface of the earth at different angles ranging from 0 degrees (no sun) at the poles to 90 degrees at the equator during spring and fall. At the equator during noon time, the earth’s surface gets the maximum amount of energy. As one moves away from the equator, the sun’s rays have to travel longer through the atmosphere. Along the way some rays are reflected into space or scattered by clouds causing loss of energy as they go. On average, about 50% of the sun’s energy makes it through the atmosphere and strikes the earth. The tilt in the earth’s axis of rotation also causes variations in the amount of sunshine received. The north pole receives little sunshine in the winter months and likewise the south pole receives little in the summer months. So the amount of solar energy that reaches any given location varies by latitude, time of year, time of day, and local weather
Solar Cell
A large majority of solar cells are made from silicon. In this section we will discuss only crystalline silicon cells (see the section in Solar In-depth for thin film types of cells). When silicon absorbs sunlight, the energy from the sun excites some of the cell’s electrons into a mobile state where they are free to move around the entire cell. However, in a piece of plain silicon there is no reason for them to go in one direction rather than another (electricity is the movement of electrons in one direction). However, in solar cells, there is a separator called a junction, where two slightly different types of silicon meet. The two types of silicon are pretty much the same, except each one is “doped” – has a tiny percentage of other materials mixed in. The two types of doping (called n-type and p-type) determine its electrical properties. When a random electron reaches the junction, it is accelerated across it (think about a waterfall … the water can only go one way – down). So this flow establishes an electron direction in the system. If a wire is attached to each side of the junction, and sunlight is absorbed by the silicon, the free electrons flow from one side of the junction to the other. This flow of electrons induces a similar flow through the external circuit. This is “electricity” — electrons flowing in a single direction through conductors. This particular flow is called a DC current.
Electricity can be thought of as the flow of electrons (current) through a copper wire under electrical pressure (voltage) and is analogous to the flow of water through a pipe. If we think of the copper wire in an electrical circuit as the pipe, then voltage is equivalent to the water pressure (pounds per square inch) and current is equivalent to the water flow rate (gallons per minute). Power is measured in watts and is the product of voltage multiplied by current. Electrical energy is power (watts) consumed over time and is expressed as kilowatt-hours (kwh). A kilowatt hour is 1000 watt hours. If a 100 watt light bulb is on for 10 hours, it uses 1 kilowatt-hour of power (100 watts times 10 hours = 1000 watt hours or 1 kilowatt-hour). Your electric bill is expressed in terms of how many kilowatt-hours are used each month